Demonstration-Bootstrapped
Autonomous Practicing
via Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning
Quick Overview
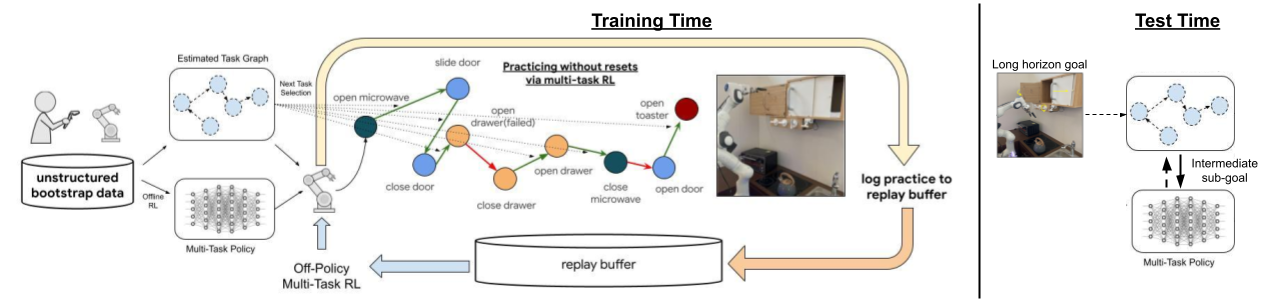
The key idea in this work is to leverage a small amount of human-provided data with multi-task reinforcement learning to build a robotic learning system that can continue improving with minimal human intervention required in the training process by practicing autonomously.
1) The human provided data is used to bootstrap a low-level goal reaching policy with offline reinforcement learning.
2) The human data is also used to build a graph that indicates which goals are reachable from other goals, which is then used to command goals for the low-level policy using a graph search algorithm.
3) The high-level goal selector continually selects goals for the low-level policy to attempt, allowing the agent to autonomously practice the behavior which leads to the overall success-rate improvement with RL, while requiring minimal human intervention.
4) The system leverages large amounts of data to improve robot behavior significantly over pre-trained offline performance and solve long horizon tasks in a kitchen environment. The provided data is used to bootstrap both the low-level goal-reaching policy and the high-level practicing mechanism.
Find a short video describing the method below:
Find a full interactive paper below:
Abstract
Reinforcement learning systems have the potential to enable continuous improvement in unstructured environments, leveraging data collected autonomously. However, in practice these systems require significant amounts of instrumentation or human intervention to learn in the real world. In this work, we propose a system for reinforcement learning that leverages multi-task reinforcement learning bootstrapped with prior data to enable continuous autonomous practicing, minimizing the number of resets needed while being able to learn temporally extended behaviors. We show how appropriately provided prior data can help bootstrap both low-level multi-task policies and strategies for sequencing these tasks one after another to enable learning with minimal resets. This mechanism enables our robotic system to practice with minimal human intervention at training time, while being able to solve long horizon tasks at test time. We show the efficacy of the proposed system on a challenging kitchen manipulation task both in simulation and the real world, demonstrating the ability to practice autonomously in order to solve temporally extended problems.
1. Introduction
Consider a robot deployed in a previously unseen kitchen, such as the one shown in Fig 1. Since this is an unfamiliar environment, the robot might not know exactly how to operate all the kitchen appliances, open cabinets, operate the microwave or turn on the burners, especially if these need to be done in a specific sequence resulting in a long-horizon task. Like many intelligent agents, the robot needs some practice, making reinforcement learning (RL) a promising paradigm. However, as we have learn from prior work, practicing long-horizon tasks with RL is difficult for reasons such as exploration
In this work, we consider the following perspective on this problem. Rather than only providing examples that aim to aid the final solution (e.g. by providing demonstrations of the final long-horizon tasks), we additionally focus on providing supervision that helps the robot to continue practicing long-horizon tasks autonomously.
In particular, we provide a set of continuous, uninterrupted multi-task demonstrations

In this paper, we present a novel robotic learning system, which we call demonstration bootstrapped autonomous practicing (DBAP), that is able to incorporate a small amount of human data provided upfront to bootstrap long periods of autonomous learning with just a few human interventions for episodic resets, using some tasks to reset others while learning how to perform long horizon behaviors. We show that just a few hours of easily-provided "play-style"(
2. Related Work
Most prior applications of RL in robotic manipulation rely on an episodic reset mechanism, which brings the robot back to a static distribution over initial states. Recent work has attempted to relax the episodic reset assumption
There are multiple approaches that aim to use demonstrations to provide a good initialization for policies via learning from demonstrations (
Long horizon problems have often been approached from the angle of hierarchical RL algorithms (
3. Preliminaries and Problem Statement
We use the standard MDP formalism (state, action, dynamics, reward, episodic horizon), but extend RL to goal-reaching tasks, where the task is represented as a state goal that the goal-conditioned policy has to reach to obtain the reward. We assume to be given a set of goal states that are of particular interest: that the agent is expected to to reach from any other state of interest, resulting in the following objective:
We often refer to reaching these goals of interests as tasks since reaching such states usually corresponds to accomplishing a meaningful task such as opening a cabinet. Note that reaching certain from would involve just short horizon behaviors spanning a single episode, while reaching other from may require long horizon reasoning over multiple different sub-steps, for instance it may require reaching on the path from to .
In order to allow for more autonomous learning with minimal human supervision, we assume that a reset can be provided every episodes (or every time steps). Our objective in this case is to train the agent in a training MDP , where resets are only received every steps such that we are able to learn a policy that is effective on the original episodic problem described in Eq. 1. This requires our learning algorithm to operate in a non-stationary setting and learn how to practice tasks mostly autonomously with only occasional resets as discussed in several prior works
AWAC: As we will discuss next, solving this problem effectively for long horizon tasks requires us to incorporate demonstrations to bootstrap both the policy and the autonomous practicing mechanism. In order to effectively incorporate prior demonstrations to bootstrap policy learning, we use the recently developed AWAC algorithm
In particular, the AWAC algorithm applies the following weighted maximum likelihood update to the actor:
where is is the advantage function, and is a hyper-parameter. Since the actor update in AWAC samples and re-weights the actions from the previous policy, it implicitly constrains the policy. We directly build on this framework for policy bootstrapping but in the following section show how we can additionally bootstrap autonomous practicing from offline data as well.
4. Demonstration Bootstrapped Autonomous Practicing for Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning

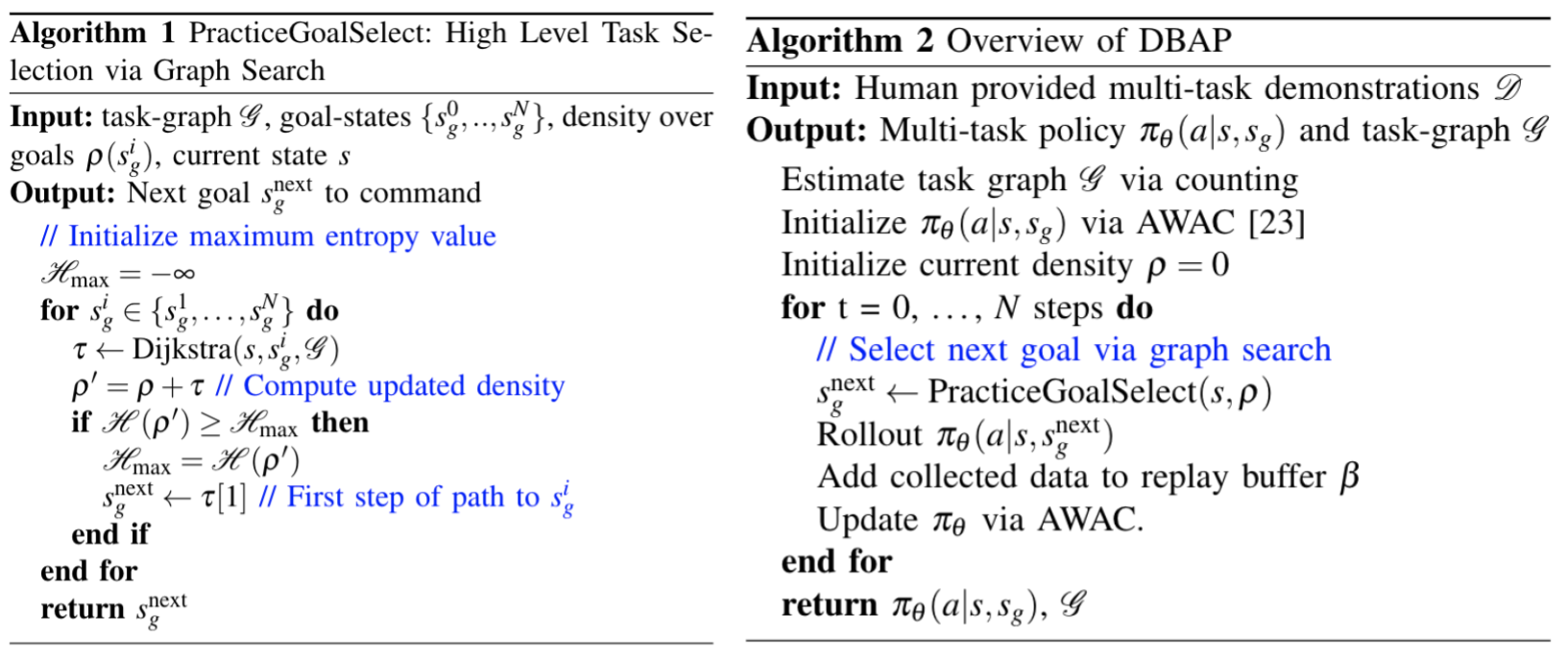
Our method, Demonstration-Bootstrapped Autonomous Practicing (DBAP) learns how to perform complex behaviors in an environment by leveraging human-provided demonstration data in two ways: to bootstrap a multi-task policy that learns to perform a variety of behaviors; and to enable a graph-based sequencing mechanism, which allows for autonomous improvement by choosing what sequence of these behaviors to command to minimize number of resets at training time. In doing so, this sequencing mechanism helps to practice each behavior at training time while also enabling the robot to sequence practiced behaviors to accomplish long-horizon tasks at test time. An overview of our overall framework is presented in Fig 2. Given a human-provided dataset, we leverage an offline RL algorithm to bootstrap a multi-task policy, while using a graph search algorithm to i) decide how to sequence tasks for practicing to improve this multi-task policy with minimal resets at training time and ii) deciding how to sequence behaviors to solve long-horizon tasks at test-time.
More precisely, we learn a single goal-conditioned policy for multiple tasks, denoted , where is a goal state. To learn this goal-conditioned policy, we instantiate a goal-conditioned version of AWAC
In order to enable agents to practice on their own with minimal number of human interventions, we require a task-sequencing policy that determines how the goals are sequenced at training time. In particular, a task-sequencing policy decides which goal of interest to command next from the current state during practicing. This resembles high-level policies used in hierarchical RL that are commonly used to sequence individual subgoals for accomplishing long-horizon goals. However, in this scenario, is not just used to accomplish long-horizon goals at test-time but also to enable autonomous practicing at training time. In the following sections we will often refer to the multi-task policy as the low-level policy, and the task sequencer as the high-level policy.
Assumptions: Before we dive into system details, we discuss some assumptions made in our problem setting. Firstly, we assume that the environment does not end up in irrecoverable states from which no action can bring the environment back to goals of interest. This assumption is common across a variety of reset-free RL algorithms
Task Sequencing via Graph Search
A successful high-level task sequencer policy is one that at training time is able to propose goals for autonomous practicing, while at test time is able to direct the agent towards reaching long-horizon goals. To learn such a task sequencer policy , we propose a simple model-based graph search algorithm. Note that is not a neural network, but the result of a search procedure. As we show empirically in our experimental evaluation, this is more flexible and robust than parameterizing directly with a neural network.
The key idea in our approach is to leverage prior data to learn which low-level task transitions are possible and can be sequenced, and then use this knowledge to optimize for both autonomous practicing (at training time) and long-horizon goal sequencing (at test time). In particular, we utilize the provided data to build a directed task graph , with vertices as different goal states of interest , , and an adjacency matrix with if there exists a transition between particular states of interest and in the demonstration data, and otherwise. This graph can be thought of as a discrete high-level model, which represents how different goal states of interest are connected to each other. Given this graph acquired from the prior data, we can then utilize it for both autonomous practicing of low-level tasks and for sequencing multiple low-level tasks to achieve multi-step goals. We describe each of these phases next.
Autonomous practicing (training time). As described in prior work
In particular, the algorithm iterates through all possible goal states of interest , determines the shortest path from the current state to the goal state via Dijkstra's algorithm
This ensures that the algorithm maintains uniform coverage over different goal states of interest in the environment, so that all tasks can be practiced equally. This process repeats at the next step, thereby performing receding horizon control (
Formally, the objective being optimized to select which goal to sequence next is given by:
where is the current marginal distribution (represented as a categorical distribution) over goal states of interest, computes the shortest distances between current state and and the goal is to bring the updated density as closer to uniform . We overload the operator here to denote an update to the density when accounting for new states.}. A detailed description can be found in Algorithm 1.
Task sequencing for long-horizon tasks (test time). Next, we ask how short-term behaviors learned by the multi-task policy can be sequenced to accomplish long-horizon goals. We note that the same graph search mechanism used for autonomous practicing at training time can be reused to sequence appropriate sub-goals at test time to accomplish long horizon tasks.
More formally, given a target goal of interest when the agent is at a particular state , we can use the estimated graph via Dijkstra's algorithm to compute the shortest path between the current state and the goal of interest , . The next goal state of interest in the path is then chosen as the next goal commanded to the multi task policy and executed for a single episode of steps till the agent reaches . This procedure is repeated until the agent accomplishes . Further details on these procedures can be found in Algorithm 1 and Algorithm 2.
5. System Description
To evaluate (DBAP) in the real world, we built a physical kitchen environment based on the simulaed kitchen manipulation benchmark described in prior work (
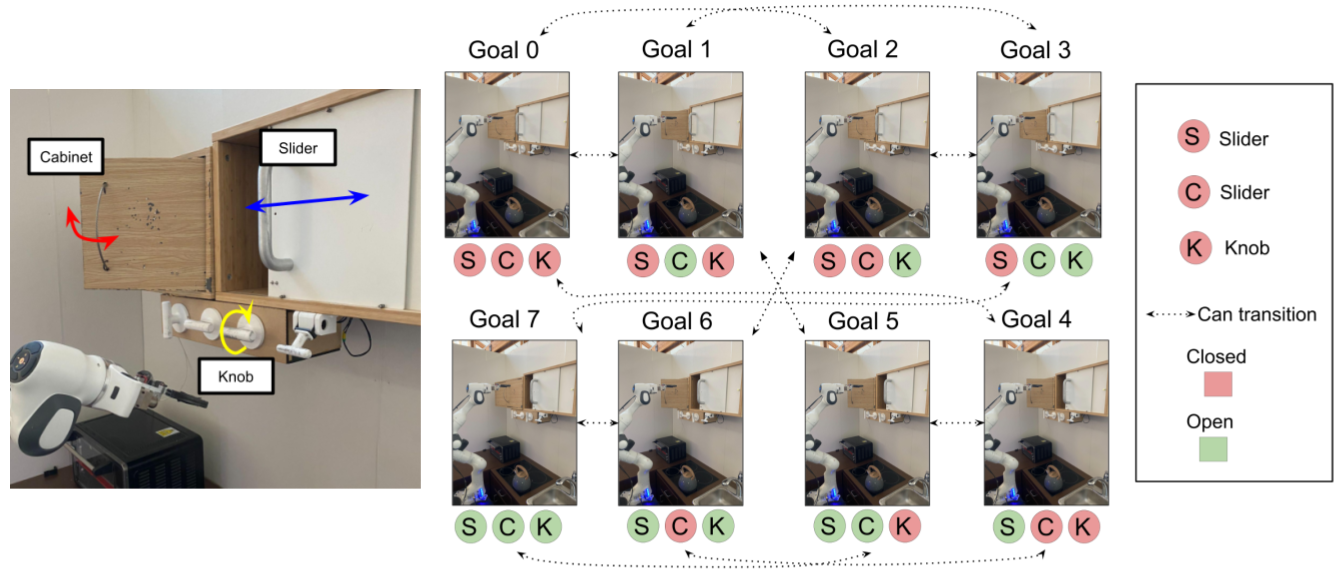

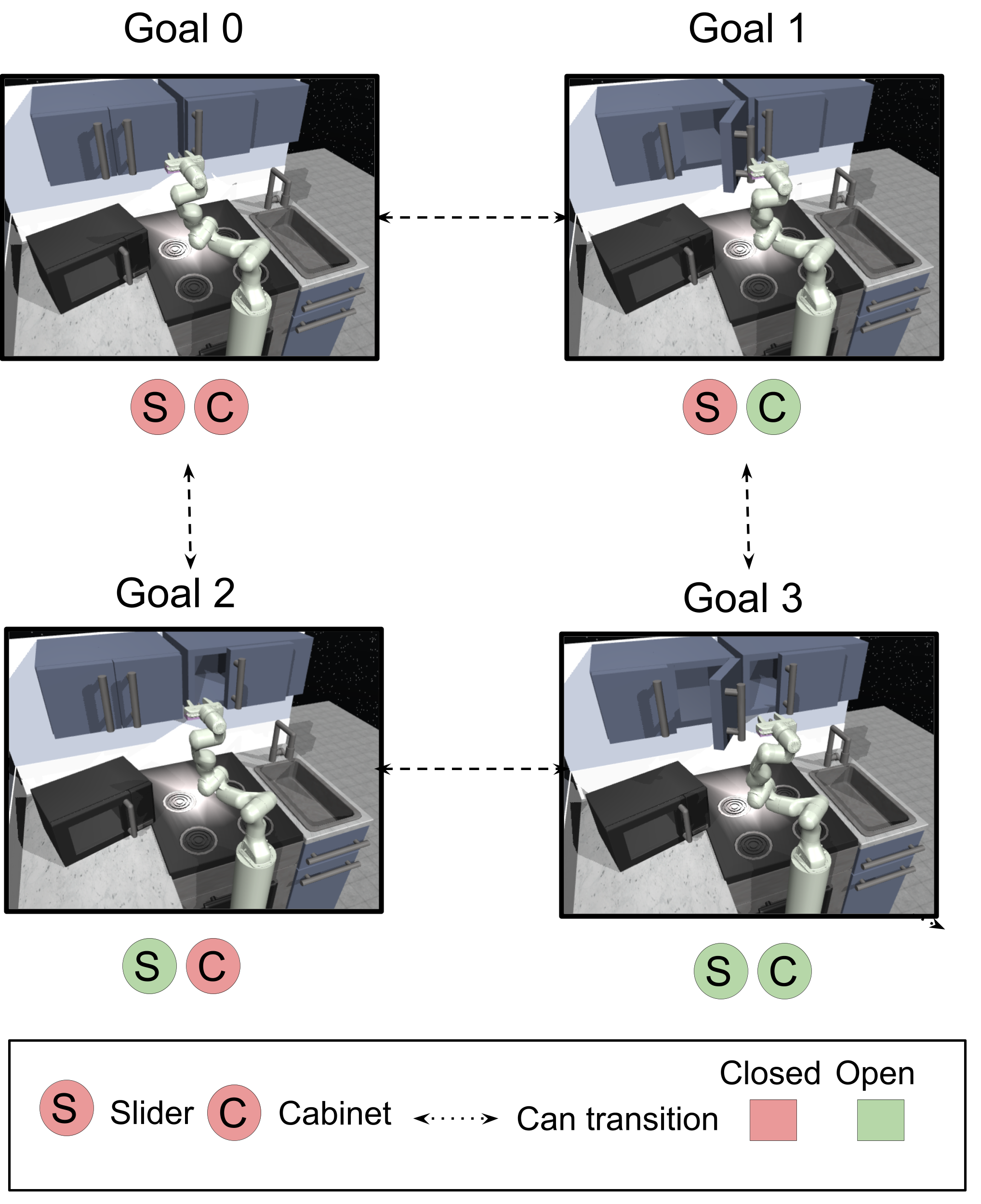
Tasks. In this environment, we task a 7 DoF Franka Emika robotic arm with manipulating three distinct elements: a sliding door that can be slid open or closed, a cabinet door that can be open or closed and a knob that can rotate to control the stove burners, as shown in Fig 4. At each time step, the policy chooses a position and orientation for the end effector, or opens/closes the gripper. These three elements represent distinct types of motion, each of which require different control strategies. The goal states of interest are defined as combinations of the elements being opened or closed (or in the case of the knob, turned by degrees or degrees), resulting in goal states based on combinations of the elements being open or closed (Fig 4).
As described in Sections 3, 4, the agent must practice reaching the goals of interest autonomously in the environment to master going from any combination of element configurations to any other. The agent is said to be in one of the goal states of interest if the current state of the elements in the scene are within distance of the goal. Long horizon goals involve flipping the state (from open to close or vice versa) of all three elements of the scene, requiring sequential reasoning.
Data collection. We make use of a teleoperation system to provide a continuous sequence of multi-task demonstrations. We collect "play-style" (
Simulation Environment
To provide thorough quantitative comparisons, we also evaluate our method on a simulated version of the above task, based on the MuJoCo kitchen manipulation environment described out by
6. Experimental Evaluation
In our experimental evaluation, we aim to answer the following questions:
- Does DBAP allow agents to learn how to perform long horizon behaviors in the real world?
- Does DBAP reduce the number of human resets required to learn long horizon behaviors, as compared to existing methods?
- Is DBAP able to use prior data to bootstrap the learning of both low-level policy execution and high level practicing behavior?
To understand the decisions made in DBAP, we compare to a number of baselines in simulation and the real world. For real-world experiments, we compare DBAP to behavior cloning without any fine-tuning (Imitation in Table 1), offline RL with AWAC without fine-tuning (Offline RL in Table 1) and the no pre-training baseline. The policies operate on a low-level state of object and end effector positions, and they are represented with 3 layer MLPs of units each.
In simulation, we use the following baselines:
i) Non-pretrained low level, graph search high level: This is a version of our algorithm, where the human-provided data is not used to bootstrap low level policies, but only the high level graph. This is related to ideas from (
ii) Pretrained low level, random high level controller: This is a multi-task analogue to the perturbation controller (
iii) Pretrained low level, BC task selection: This is a version of the method by (
iv) Pretrained low level, reset controller:
This baseline is similar to a reset controller (
v) Imitation low level, imitation high level: This baseline involves training the low level and high level policies purely with imitation learning and running an offline evaluation of how well the policy performs (as in
vi) Full relabeled relay policy learning (Gupta et al.): It involves training the RPL algorithm (
Evaluation metrics
We evaluate over multiple long horizon goal reaching manipulation tasks in the real world environment shown in Fig 4 and simulation environment shown in Fig 5. Our real world environment has three elements (cabinet, knob, and slider) and we consider two possible goal states per element (fully open or fully closed). Each long horizon task requires changing the original state of the environment to the inverted goal state. Success requires that a given task sequencer chain multiple low-level goal reaching behaviors to accomplish the long-horizon goal. For example, given original state "cabinet open, knob open, and slider closed", the goal state would be "cabinet closed, knob closed, and slider open". We construct 8 long horizon tasks in this manner and report the average success rate.
Demonstration-Bootstrapped Practicing in Real World
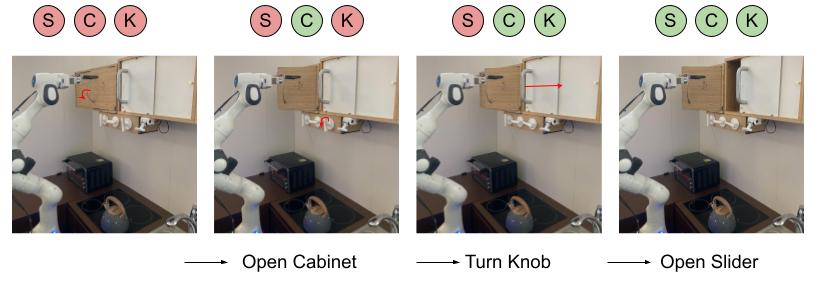
We start by evaluating the ability of DBAP to learn multiple long horizon goal-reaching tasks in the real world. We trained the robot for over hours as described in Section 4, only requiring a reset every trajectories (in wall-clock time corresponding to once an hour only). This makes training much more practical in terms of human effort.
As seen from the evaluation performance of offline RL on long horizon success in Table 1, DBAP starts off doing reasonably well during pre-training, achieving a success rate, but improves significantly during autonomous practicing (with only very occasional resets) to around a success rate, indicating the importance of online fine-tuning. In Fig 6, we show a qualitative example of DBAP succeeding at one of the 8 long horizon tasks, where the robot must reach a goal with slider, cabinet, and microwave door all open, from a state where all three are closed. The graph search automatically commands the low-level policy to reach each of the subgoals for the complete task.
In comparison, the no-pretraining, from-scratch baseline results in 0% success rate. This indicates the importance of being able to incorporate prior data, as is done in DBAP, to overcome hard exploration challenges inherent in long horizon manipulation. DBAP also significantly outperforms imitation learning in terms of long horizon goal-reaching performance. We compare the number of tasks commanded to accomplish the multi-step goals and observe the average path length is significantly lower for our method than baselines.
| Success Rate | Path Length | |
|---|---|---|
| Offline RL | 0.83 | 3.5 |
| DBAP (Ours) | 0.95 | 3.37 |
| Imitation | 0.62 | 4.3 |
| No Pretraining | 0.0 | 6.0 |
Table 1: Success rates and path lengths (in number of steps) in the real world for reaching long horizon goals. Higher success rate is better and lower path length is better.
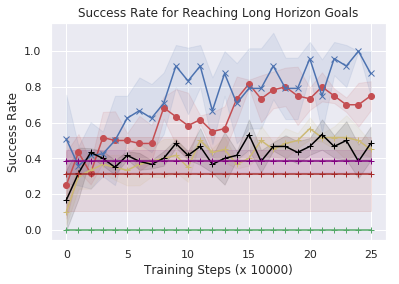
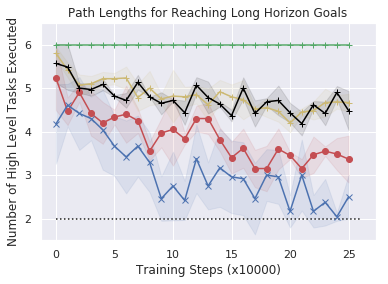
Demonstration-Bootstrapped Practicing in Simulation
Next, to study comparisons with baselines more systematically we evaluate the ability of DBAP to learn to accomplish multi-step goals in simulation as described in Section 5, with a minimal amounts of automatically provided resets. In simulation we assume access to one human reset every episodes, reducing the amount of human supervision by an order of magnitude as compared to standard RL. As shown in Fig 7 (left), our method successfully reaches a variety of multi-step goals and shows improvement over time with minimal human involvement (from to success rate). While other techniques are able to occasionally succeed, they take significantly longer to get to the goal, often resulting in roundabout paths to achieve the goal. This leads to the extended path length of trajectories in Fig 7(middle). Training a high level policy via goal relabeling and BC (the "pretrained low-level, BC task selection" and "full relabeled relay policy learning" baseline in Fig 10.) can inherit the biases of the data. If the play data demonstrates sub-optimal paths to reach long horizon goals, this is reflected in the performance of the high-level BC. This also happens for the offline imitation learning baseline, indicating it is not a facet of offline reinforcement learning. In contrast, our graph-based search method is able to find and practice shorter paths than the baselines. Importantly, this improvement is acquired with a minimal requirement for human effort in the process.
These studies suggest that DBAP is able to both enable autonomous practicing with minimal human effort and via this practicing enable a real world robotic agent to solve long horizon tasks by sequencing subgoals appropriately.
Conclusion
We leverage human-provided data to bootstrap a multi-task RL system, using some tasks to provide resets for others. Our method combines offline RL at the low level and model-based graph search at the high level, where prior data is used to bootstrap low-level policies as well as facilitate practicing. We demonstrated the success of this system on both simulated and real-world kitchen environments.
However, this work has several limitations. It requires tasks to be discretely defined, which is done by thresholding low-level states. Extending to high dimensional problems is an interesting avenue for future work. The algorithm assumes that the environment does not transition into "irreversible" states. This assumption is common in reset-free RL (